Strength training exercises, yo! Get ready to pump up those muscles and take your fitness game to the next level. From bone health to athletic performance, we’re diving into it all.
Let’s break down the different types of exercises, proper form techniques, nutrition tips, and the importance of recovery in a complete strength training regimen.
Benefits of Strength Training Exercises

Strength training is crucial for overall fitness as it helps build muscle mass, increase metabolism, and improve body composition. It is not just about lifting heavy weights but also about functional movements that enhance daily activities.
Weight Management
Strength training plays a key role in weight management by increasing muscle mass, which in turn boosts metabolism. This leads to more calories burned throughout the day, even at rest. Additionally, strength training helps maintain muscle mass while losing fat, resulting in a toned and fit physique.
Bone Health
Engaging in regular strength training exercises can significantly improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Weight-bearing exercises like squats, lunges, and deadlifts stimulate bone growth, making them stronger and less prone to fractures.
Athletic Performance
Strength training enhances athletic performance by increasing power, speed, agility, and endurance. Stronger muscles provide better support and stability during physical activities, leading to improved overall performance in sports and other physical pursuits.
Types of Strength Training Exercises
Strength training exercises come in various forms, each targeting different muscle groups and providing unique benefits. Here are some examples of different types of strength training exercises:
Compound Exercises
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together. These exercises are effective for building overall strength and muscle mass. Examples of compound exercises include squats, deadlifts, bench press, and pull-ups.
Free Weights vs Machines
Free weights, such as dumbbells and barbells, require stabilizing muscles to work harder, providing a more functional strength workout. Machines, on the other hand, guide your movement, making it easier to isolate specific muscles. Both have their benefits, and a combination of both can be effective in a strength training routine.
Push-up Variations
Push-ups are a classic bodyweight exercise that strengthens the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Variations like incline push-ups, decline push-ups, diamond push-ups, and plyometric push-ups can target different muscle groups and add variety to your workout routine.
Resistance Bands, Strength training exercises
Incorporating resistance bands into your strength training routine can provide added resistance to exercises, helping to improve muscle strength and endurance. Resistance bands are versatile, portable, and can target specific muscle groups effectively. They are great for adding variety and intensity to your workouts.
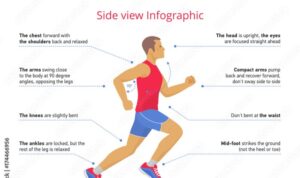
Form and Technique in Strength Training

Proper form and technique are essential in strength training to prevent injuries and maximize the effectiveness of your workouts.
Significance of Proper Form
Maintaining proper form during strength training exercises is crucial to avoid strain on muscles and joints. It helps target the intended muscle groups and reduces the risk of injury.
- Keep your back straight and engage your core to support your spine.
- Avoid using momentum to lift weights; focus on controlled movements.
- Ensure proper alignment of joints to prevent unnecessary stress.
Tips for Correct Posture
Maintaining correct posture is key to getting the most out of your strength training workouts and preventing injuries.
Remember to align your ears, shoulders, hips, and ankles in a straight line for exercises like squats and deadlifts.
Importance of Breathing Techniques
Proper breathing techniques play a vital role in strength training as they help stabilize your core and provide oxygen to your muscles.
- Breathe in during the eccentric (lowering) phase and exhale during the concentric (lifting) phase of an exercise.
- Avoid holding your breath, as it can increase blood pressure and reduce oxygen supply to your muscles.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes that people make during strength training exercises that can hinder progress and increase the risk of injury.
- Avoid using weights that are too heavy, compromising your form.
- Don’t rush through exercises; focus on controlled movements and full range of motion.
- Avoid hyperextending joints or rounding your back during exercises.
Nutrition and Recovery for Strength Training: Strength Training Exercises
Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting muscle growth and recovery after intense strength training sessions. By providing your body with the right nutrients, you can optimize muscle repair and enhance your overall performance.
Role of Nutrition in Muscle Growth and Recovery
Proper nutrition is essential for repairing and building muscle tissue. Consuming an adequate amount of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats can help fuel your workouts and aid in muscle recovery. Protein, in particular, is vital for repairing and building muscle fibers damaged during strength training.
Post-Workout Nutrition Tips
– Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to replenish fluids lost during exercise.
– Protein intake: Consume a protein-rich snack or meal within 30 minutes to an hour after your workout to support muscle repair.
– Carbohydrates: Include complex carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores and provide energy for recovery.
– Nutrient-dense foods: Opt for whole foods like lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for optimal recovery.
Importance of Rest Days
Rest days are crucial in a strength training routine as they allow your muscles to recover and grow stronger. Overtraining can lead to muscle fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. Make sure to incorporate rest days into your training schedule to give your body the time it needs to repair and rebuild muscle tissue.
Foods for Muscle Repair and Growth
– Lean proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt
– Complex carbohydrates: Brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, whole grain bread
– Healthy fats: Avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil
– Antioxidant-rich foods: Berries, leafy greens, colorful vegetables