Diving into the world of crypto mining techniques, get ready to uncover the evolution of mining, popular algorithms, hardware requirements, and the dynamics of mining pools. It’s time to explore the ins and outs of this cutting-edge digital frontier.
Overview of Crypto Mining Techniques
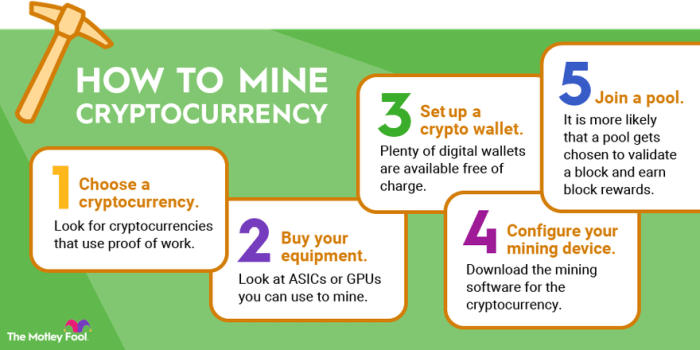
Crypto mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the public ledger (blockchain) through complex mathematical computations. Miners use powerful computers to solve these algorithms and are rewarded with new cryptocurrency coins for their efforts.
Importance of crypto mining in the blockchain ecosystem:
– Crypto mining plays a crucial role in securing and decentralizing the blockchain network by verifying transactions.
– Miners help maintain the integrity of the ledger and prevent double-spending of digital assets.
– The mining process incentivizes individuals to participate in the network and contribute to its operation and security.
Evolution of crypto mining techniques:
From CPU to ASIC Mining
In the early days of Bitcoin, mining could be done using a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). However, as the network grew, miners shifted to more powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) for faster computations. Eventually, specialized hardware known as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) were developed, significantly increasing mining efficiency and speed.
Popular Crypto Mining Algorithms
Cryptocurrency mining relies on various algorithms to validate transactions and secure the network. Some of the most commonly used mining algorithms in the cryptocurrency space include:
SHA-256
SHA-256 is used by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. It is a proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm that requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks in the blockchain.
Ethash
Ethash is the mining algorithm used by Ethereum. It is also a PoW algorithm but differs from SHA-256 in its memory-hardness, making it more resistant to ASIC mining.
X11, Crypto mining techniques
X11 is a hashing algorithm used by Dash and several other cryptocurrencies. It is a chained algorithm that consists of 11 different cryptographic algorithms, providing increased security and energy efficiency compared to other algorithms.
Proof-of-Work (PoW) vs. Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are two common consensus algorithms used in blockchain networks. PoW requires miners to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions, while PoS validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold. PoW is more energy-intensive compared to PoS, as it requires computational power to solve puzzles.
Impact on Energy Consumption
Mining algorithms play a significant role in determining the energy consumption of cryptocurrency mining. PoW algorithms, such as SHA-256, require high computational power and energy consumption, leading to concerns about environmental impact. PoS algorithms, on the other hand, are more energy-efficient as they do not rely on computational power for validation.
Hardware Requirements for Crypto Mining

To effectively mine cryptocurrencies, specific hardware components are essential for efficient processing and mining operations. These components play a crucial role in determining the speed, efficiency, and profitability of the mining process.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs)
- GPUs are commonly used in crypto mining due to their parallel processing power, making them ideal for handling complex mathematical calculations required for mining.
- They are preferred for mining algorithms that are memory-intensive, such as Ethereum’s Ethash algorithm.
Central Processing Units (CPUs)
- CPUs are used in certain mining setups, although they are not as efficient as GPUs due to their sequential processing nature.
- CPUs are typically used for mining algorithms that are less complex and require more general-purpose processing.
Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) Miners
- ASIC miners are specialized hardware designed specifically for mining cryptocurrencies.
- They are highly efficient and are particularly suited for mining algorithms like SHA-256, used for Bitcoin mining.
Other Hardware Components
- In addition to GPUs, CPUs, and ASIC miners, other hardware components such as motherboards, power supplies, cooling systems, and storage devices are crucial for building a mining rig.
- Advancements in hardware technology, such as the development of more powerful GPUs and ASIC miners, have significantly impacted the efficiency and profitability of crypto mining operations.
Mining Pools and Solo Mining: Crypto Mining Techniques
When it comes to crypto mining, miners have the option to join a mining pool or mine solo. Let’s dive into the details of each option.
Mining Pools
Joining a mining pool involves combining computational resources with other miners to increase the chances of successfully mining a block. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of mining pools:
- Advantages:
- Increased chances of earning rewards due to combined computational power.
- Regular and more predictable payouts compared to solo mining.
- Access to advanced mining software and hardware through the pool.
- Disadvantages:
- Sharing rewards with other pool members.
- Potential for centralization of mining power within the pool.
- Possibility of pool fees reducing overall profits.
Popular Mining Pools
Some of the popular mining pools in the crypto mining community include:
- Slush Pool: One of the oldest mining pools that offers a secure and reliable platform for miners.
- F2Pool: A global mining pool that supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies.
- AntPool: Known for its high hash rate and frequent payouts.
Solo Mining
Solo mining involves mining independently without joining a pool. Here are some key points to consider:
- Advantages:
- Full control over mining operations and rewards.
- No need to share rewards with others.
- Potential for higher profits if blocks are successfully mined.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower chances of mining a block due to less computational power.
- Irregular payouts and longer waiting periods for rewards.
- Higher risk of not earning any rewards if mining efforts are unsuccessful.