Car financing options open up a world of possibilities when it comes to getting behind the wheel of your dream car. From traditional auto loans to lease financing and dealership options, the road to car ownership is paved with choices. Dive into the details and discover the best route for you!
Car Financing Options Overview
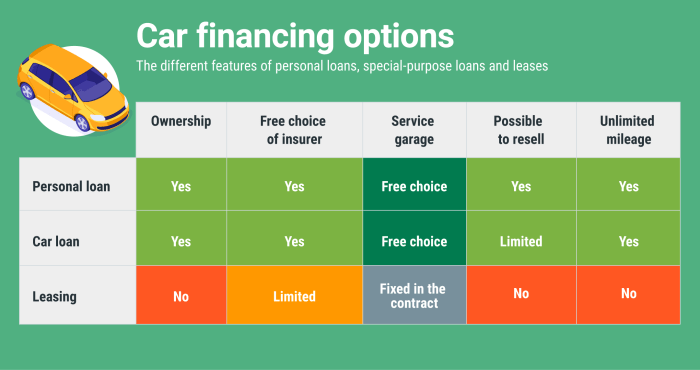
When it comes to buying a car, not everyone has the cash upfront to make the purchase. That’s where car financing comes in. Car financing allows individuals to spread out the cost of a vehicle over time, making it more affordable for them to own a car.
Types of Car Financing Options
- Auto Loans: Auto loans are one of the most common forms of car financing. With an auto loan, the borrower receives a lump sum of money from a lender to purchase a vehicle. The borrower then makes monthly payments to repay the loan over a set period, usually with interest.
- Leasing: Leasing is another popular option where the individual essentially rents the car for a set period of time. Monthly payments are made to the leasing company, and at the end of the lease term, the car is returned.
- Dealer Financing: Dealer financing is when the car dealership assists in arranging a loan for the buyer. The dealership works with various lenders to find the best financing option for the buyer.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Car Financing Options
- Auto Loans: Benefits include ownership of the vehicle at the end of the loan term. Drawbacks may include higher monthly payments due to interest.
- Leasing: Benefits include lower monthly payments and the ability to drive a newer car more frequently. Drawbacks may include mileage restrictions and no ownership of the vehicle.
- Dealer Financing: Benefits include convenience and the ability to negotiate terms with the dealership. Drawbacks may include higher interest rates compared to other lenders.
How Car Financing Works in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, car financing plays a crucial role in driving sales. Dealerships often offer special financing deals to attract customers and promote sales. Lenders work with buyers to assess creditworthiness and determine loan terms. Understanding how car financing works can help individuals make informed decisions when purchasing a vehicle.
Traditional Auto Loans: Car Financing Options
When it comes to financing a car, traditional auto loans are a popular choice for many buyers. These loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders, and they work by lending you a specific amount of money to purchase a vehicle, which you then pay back over time with interest.
How Traditional Auto Loans Work
- Traditional auto loans come in two main types: fixed-rate and variable-rate loans.
- Fixed-rate loans have a set interest rate that remains the same throughout the loan term, making it easier to budget for your monthly payments.
- Variable-rate loans, on the other hand, have an interest rate that can fluctuate based on the market, which can lead to changes in your monthly payments.
Applying for a Traditional Auto Loan
- When applying for a traditional auto loan, you will need to provide personal information such as your name, address, income, and employment details.
- You may also need to provide information about the vehicle you want to purchase, including the make, model, and VIN number.
- The lender will also check your credit score to determine your eligibility for the loan and the interest rate you will be offered.
Role of Credit Scores
- Credit scores play a significant role in securing a traditional auto loan. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine the interest rate you qualify for.
- A higher credit score typically results in a lower interest rate, while a lower credit score may lead to higher interest rates or even denial of the loan.
- It’s essential to check your credit score before applying for a traditional auto loan and work on improving it if needed to secure better loan terms.
Lease Financing

Lease financing is a popular option for acquiring a vehicle without the long-term commitment of ownership. Unlike traditional auto loans where you eventually own the car after payments, leasing allows you to essentially rent the vehicle for a set period.
Advantages of Leasing a Car
- Lower monthly payments compared to auto loans.
- Ability to drive a new car every few years.
- No worries about depreciation as you can return the car at the end of the lease.
Disadvantages of Leasing a Car
- Mileage restrictions can result in extra charges if exceeded.
- You don’t own the car at the end of the lease.
- Costly fees for wear and tear beyond normal use.
Lease Terms and End-of-Lease Options
Lease terms typically range from 2 to 4 years, with the option to buy the car at the end of the lease period. You may also have the choice to return the car and lease a new one or extend the lease on the current vehicle.
Financial Implications of Leasing vs. Buying
Leasing a car often results in lower monthly payments but can end up costing more in the long run compared to buying. With leasing, you’re essentially paying for the depreciation of the vehicle during the lease period, while owning a car allows you to build equity over time. Consider your driving habits and financial goals when deciding between leasing and buying a car.
Dealership Financing
When it comes to buying a car, dealership financing can be a convenient option for many buyers. Dealerships often offer in-house financing as well as third-party financing options to help customers secure the funds they need to purchase a vehicle.
In-house Financing vs. Third-Party Financing
In-house financing is when the dealership itself provides the loan to the buyer, while third-party financing involves working with an external financial institution, such as a bank or credit union. In-house financing may be more flexible in terms of credit requirements but could come with higher interest rates. Third-party financing, on the other hand, may offer lower rates but stricter credit criteria.
Negotiating Financing Terms, Car financing options
– Come prepared with your credit score and pre-approved loan offers from other financial institutions.
– Be willing to negotiate not just the monthly payments but also the interest rate and loan term.
– Don’t focus solely on the monthly payments, consider the overall cost of the loan including interest.
– Be prepared to walk away if the terms offered are not favorable to you.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
– Falling for the “low monthly payment” trap without considering the total cost of the loan.
– Signing a contract without fully understanding the terms and conditions.
– Accepting add-ons or extras in the financing package that you don’t really need.
– Not shopping around for better financing options before committing to a dealership offer.





